Cambridge Design and Technology students have to be familiar with how to cut, shape and form plastic using a range of different methods. This article introduces various plastic forming processes, including vacuum forming, blow moulding, injection moulding, line bending and so on, helping students prepare for examination questions on this topic.
Note: A pencil cannot be used to mark out plastics – a felt pen should be used to make out plastic instead (this can be wiped off afterwards – don’t use a vivid or permanent marker as it will leave marks all over the plastic)!
Vacuum forming
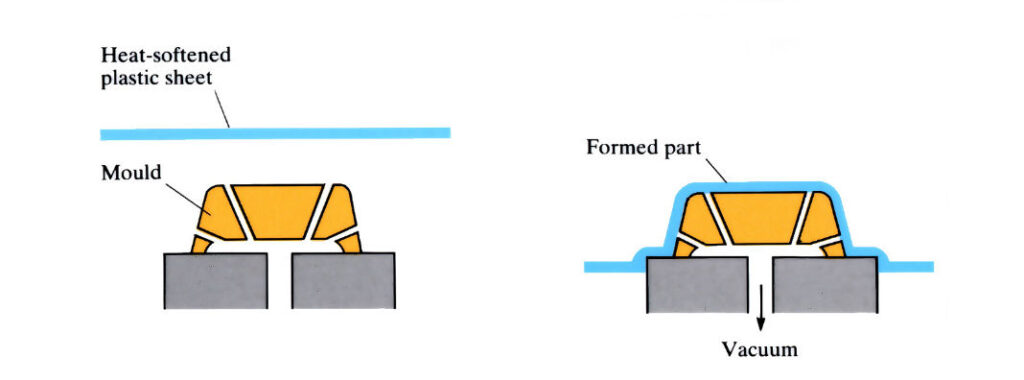
- Thin plastic sheet (i.e. PVC) is heated and sucked down around a ‘former’ (mould)
- See detailed information about vacuum forming
- Only works for thin plastic and relatively simple moulds
- Commonly used for blister packaging
Shrink wrapping
- Wrap product with plastic film (i.e. PVC or PE)
- Apply heat using a heat gun or pass through a heat tunnel to warm the plastic
- Plastic shrinks and contracts, pulling tight around the product’s shape
- Forms tight protective seal – used as protective packaging – often holds multiple products together
Laser cutting and engraving
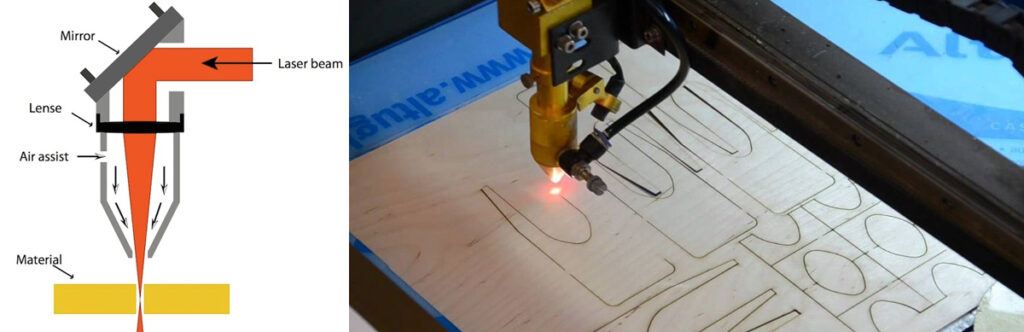
- File created using CAD software such as Techsoft Design or Adobe Illustrator (different colour used for cutting and engraving)
- Sheet of material placed in bed of laser cutter, depth set correctly
- Extraction fan turned on
- File sent to laser cutter, ensuring to enter speed and other settings as appropriate for that material according to manual
- Material laser cut / engraved and lifted from bed, removing all scraps and debris
Vinyl cutting
Thin sheets of vinyl can be cut using a vinyl cutter. Learn more about vinyl cutting in the article about cutting lightweight materials.
Blow moulding
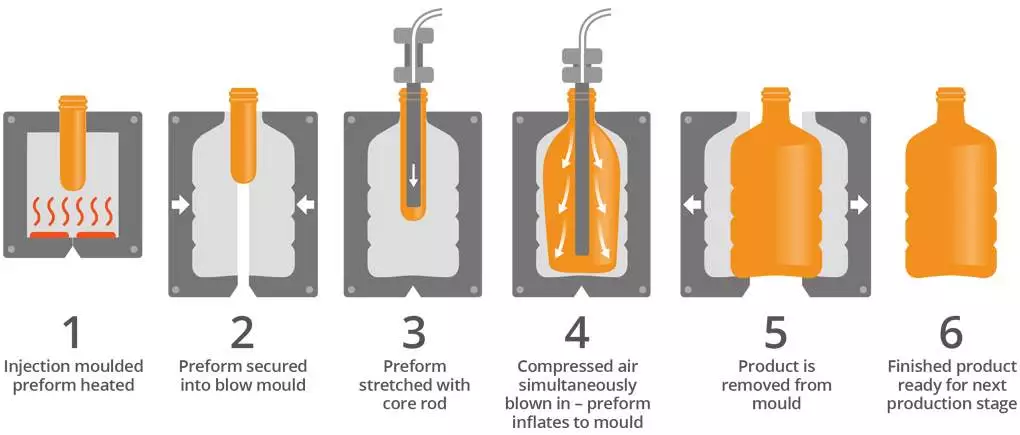
- Molten tube of plastic lowered into a mould
- Blow air in through tube, so it inflates and presses against the walls of the mould (like blowing up a balloon)
- Cool and harden
- Open mould and remove
- Creates hollow plastic parts in one piece
- Commonly used for bottles and containers
Injection moulding
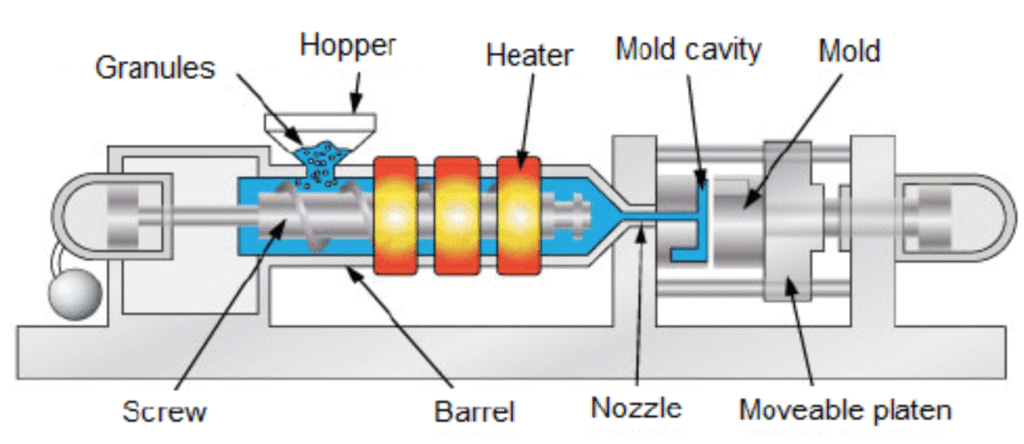
- Plastic granules are fed into machine via a hopper (funnel-shaped container that sits on top of the machine)
- Plastic pellets are heated until they become liquid
- Molten plastic is injected into a closed mould using high pressure (two halves of mould that clamp together)
- Cools and harden inside the mould
- Mould opened to release the part
- Widely used
- Fast production, with consistent quality and accurate dimensions
- High costs to set up (not good for short runs)
Extrusion
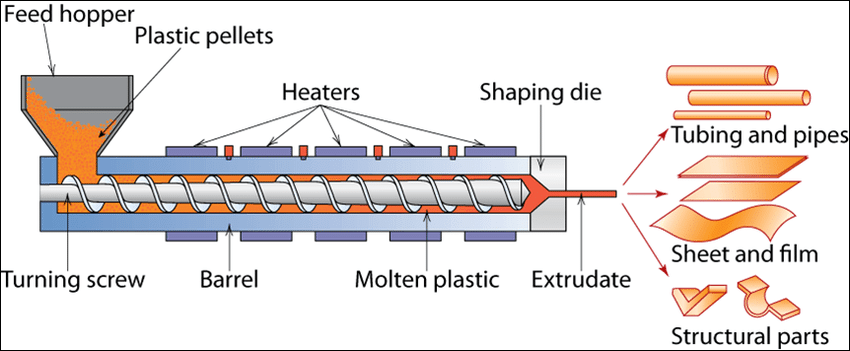
- Plastic granules are fed into machine via a hopper (funnel-shaped container that sits on top of the machine)
- Machine is hot and melts plastic
- Molten plastic is pushed through a die with a shaped metal opening using a rotating screw
- Continuous shape emerges – a long, continuous profile matching the shape of the die (like squeezing toothpaste from a tube)
- Plastic cools and hardens as it moves out
- Cut to length as required
A die is a pre-made metal plate or block that shapes material – sometimes by flowing through it (hole), sometimes by cutting it (sharp edge – i.e. a die cutter), and sometimes by pressing/forming it (solid shaping surface).
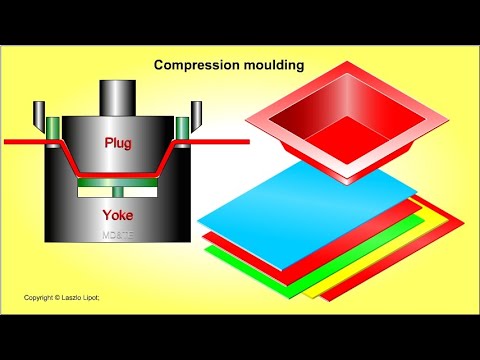
Compression moulding
3D printing
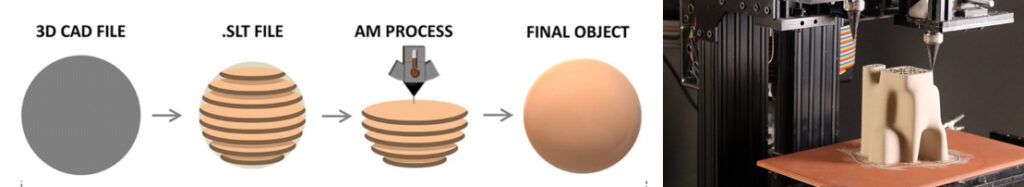
- Create digital 3D model using appropriate CAD software such as Blender
- Save file as STL file
- Slice into layers using software linked to 3D printer such as Bambu Studio and add ‘supports’ as necessary
- Send file to 3D printer which heats plastic filament until molten and prints model layer by layer
- Remove printed item, clean the build plate and remove any support material
Line bending
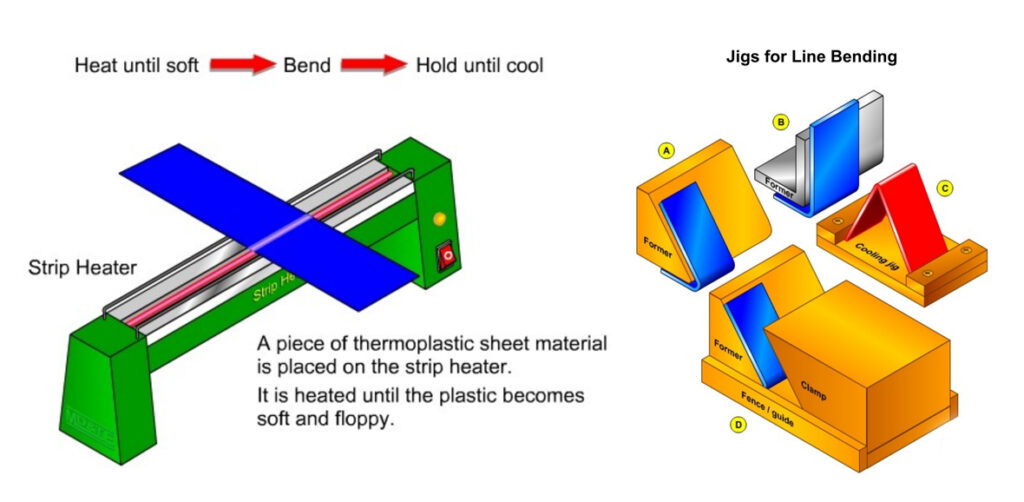
- A strip heater is used to heat the plastic in a line, so that it can be bent
- Use a jig and/or former to help bend the item over the edge of a table or around a former, and hold the item in shape while it cools
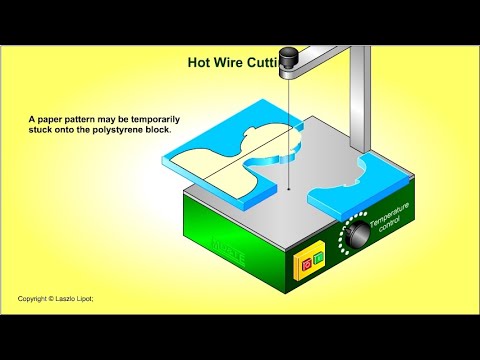
Hot wire cutting
Expanded polystyrene can be cut using a hot wire cutter, but fumes are toxic (forced air-extraction must be used and never do when wire is red-hot, as melts it too much, decomposes, toxic fumes, and fire risk).
Bandsaw or handsaw
- Can be used to cut plastics such as acrylic sheet or Styrofoam sheets (see the article about shaping wood for more information about these tools)
- When cutting acrylic, this makes a rougher edge than cutting with a laser cutter, which then needs sanding (see below).
Manual cutting (scissors or guillotine)
- Only suitable for one-off creations, or very small batches
Wet and Dry sandpaper
- A special type of sandpaper that can be used either dry or wet.
- Often used wet to stop the sandpaper clogging with plastic dust.
Brasso
- A metal polish (the name comes from “brass”) that you put on a cloth and rub onto metal to clean / polish door handles / instruments / stainless steel items etc (remove oxidation and make them shiny)
- Can be used on cut edges of acrylic to remove fine scratches and make a clear, shiny edge
- Cannot be used on wood as it is oily and stains the surface
- Give the acrylic a professional, transparent appearance
- The sequence would typically be: cut the acrylic with the bandsaw → smooth edges with wet and dry sandpaper (progressing through finer grades) → final polish with Brasso to achieve clear, professional-looking edges on the elephant ears.
Sample examination questions (AS Design & Technology)
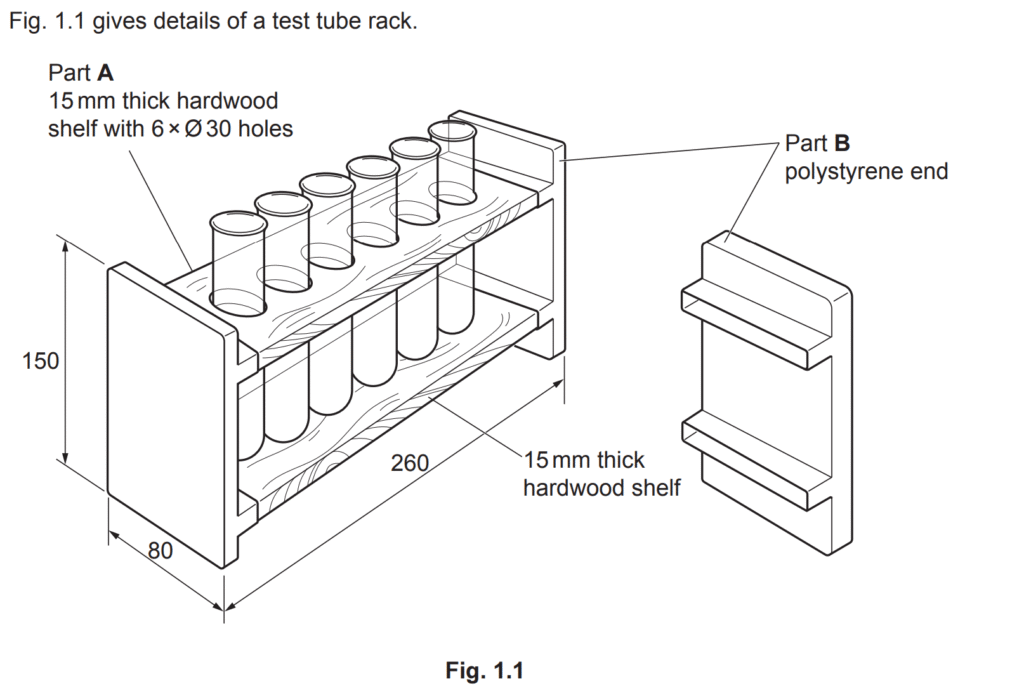



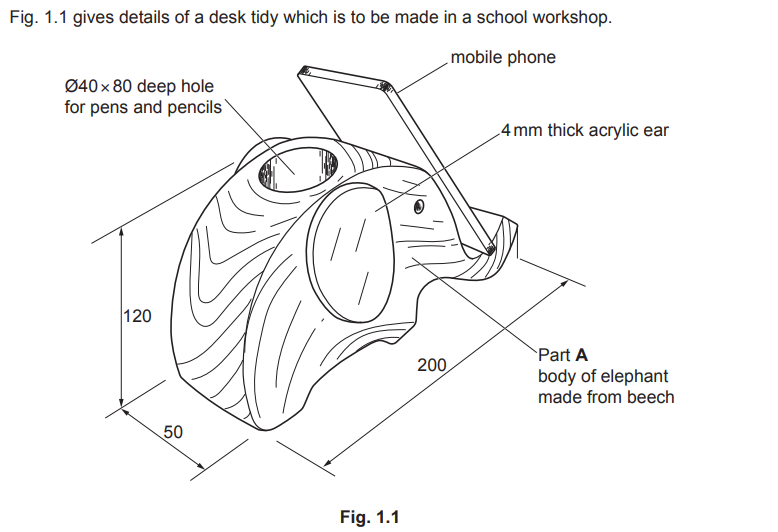


Examiner comment: This was a very well answered question with candidates demonstrating a good knowledge of how to make two identical ears. There were some very good responses that detailed how using a template or clamping the two parts enabled a more accurate outcome. Attaching the ears to the elephant was occasionally not undertaken.
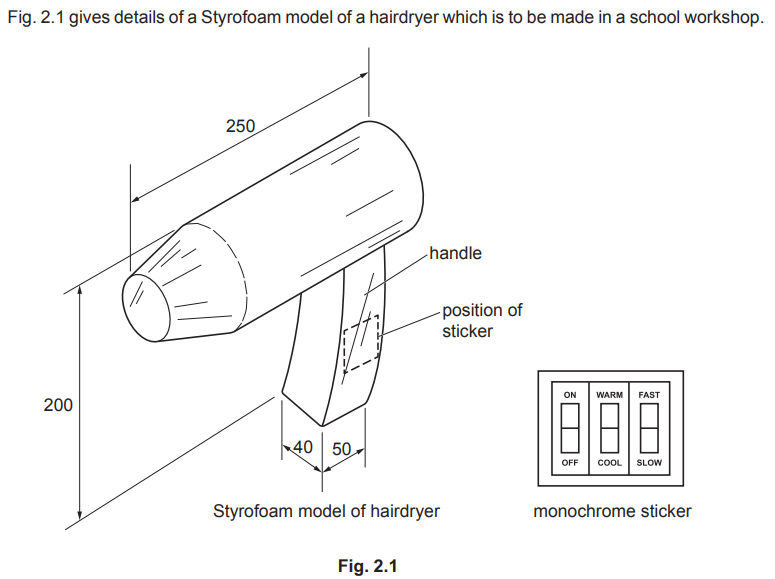



Examiner comment: Generally, this question was answered well with candidates understanding how to make the handle from a sheet of 20 mm Styrofoam. Marking out, cutting and finishing techniques were all well communicated but some candidates did not recognise that two sheets needed to be stuck together
to give the overall thickness of the handle.





Examiner comment: Candidates had a good understanding of how to smooth the model and apply a paint finish. However, some candidates decided to apply an aerosol spray finish which was incorrect.
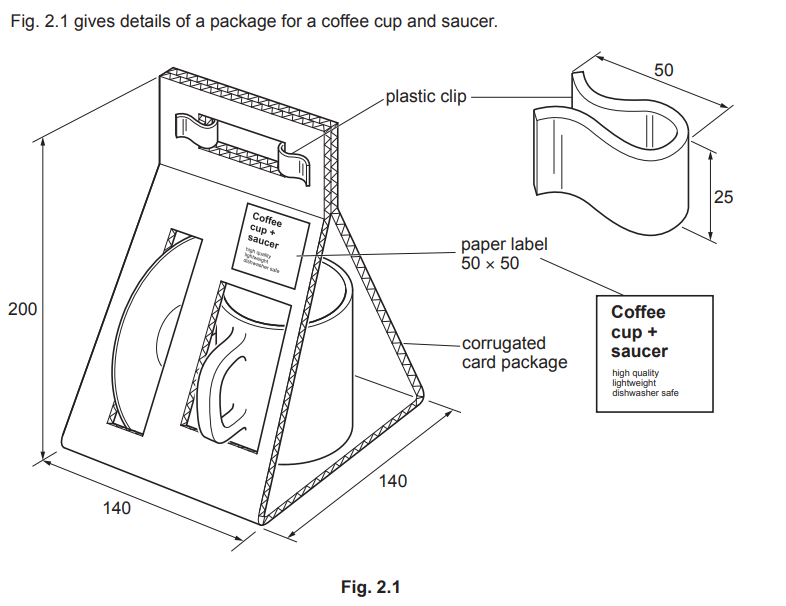


Examiner comment: Candidates were able to name a specific plastic for the clip. However, some candidates did not give a suitable process to make a batch of 5000 clips. When injection moulding was given as an answer, candidates tended to score very well indeed.
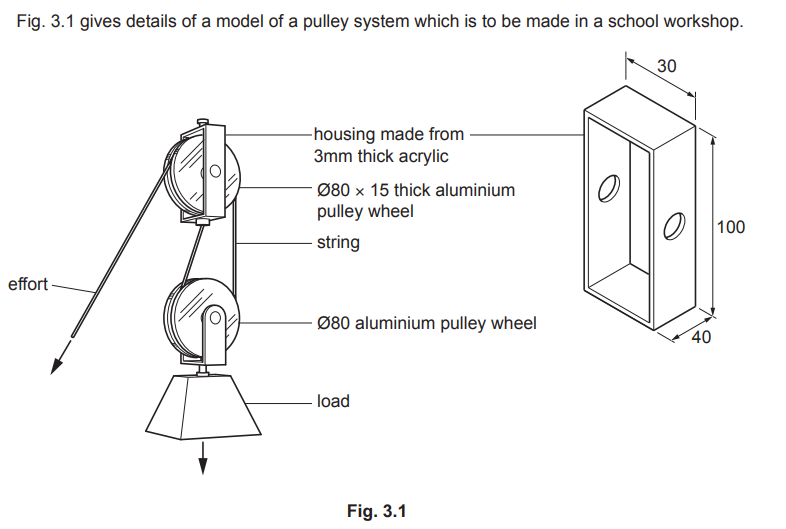



Examiner comment: Candidates were generally able to explain how to make Part A, with the use of a strip heater for folding up the acrylic housing being regularly stated.
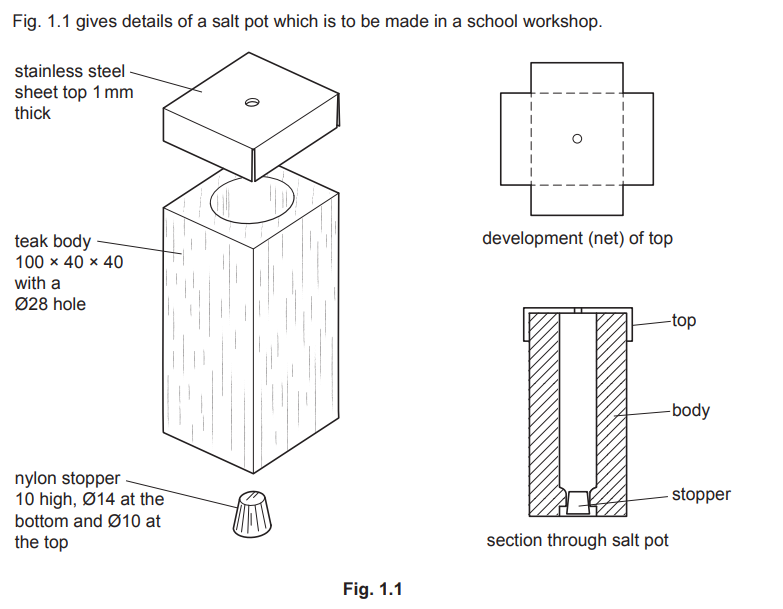


Examiner comment: Candidates found it challenging to show how to produce 5000 nylon stoppers. Stronger candidates had a good understanding of injection moulding.
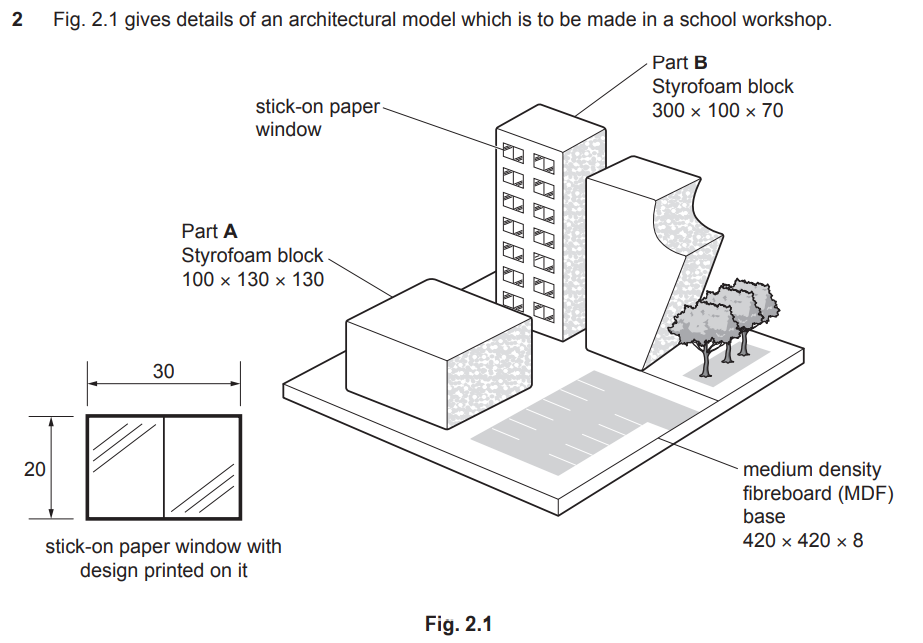

Examiner comment: Most candidates answered this well and understood how to mark out, cut, glue, clamp and sand part A. Technical terms for tools and equipment were often clearly identified.
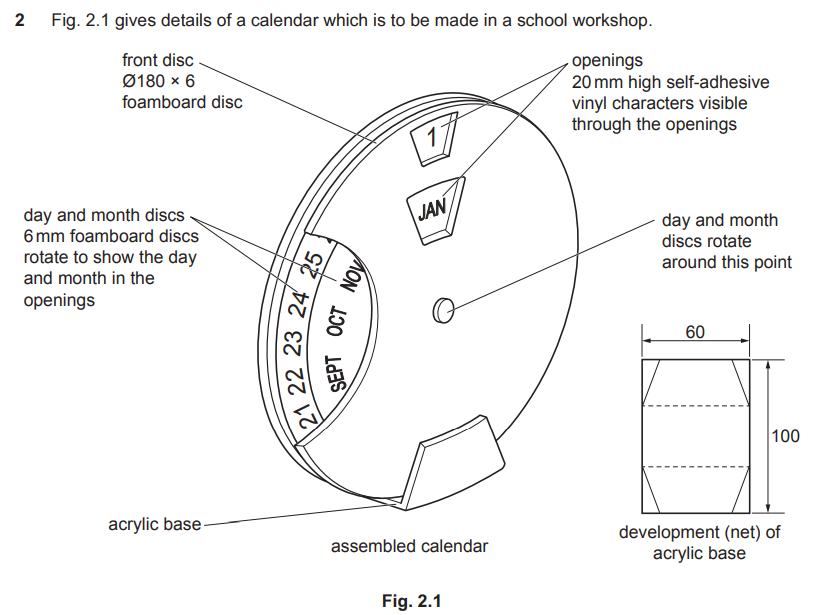



Examiner comment: Candidates gave a wide variety of answers to this question. Stronger answers included marking out, cutting out and then using a line bender to fold the acrylic.