Design & Technology students often use a range of hardwoods, softwoods, and manufactured boards. This article summarises the properties, stock forms, and uses of timbers and manufactured boards, helping students to revise these topics. It concludes with sample examination questions from the Cambridge AS/A Level syllabus.

How is timber made?
- Trees are harvested (cut down, stripped of branches, and trunks cut to lengths that fit on a truck)
- Logs are sliced lengthways using a sawmill (freshly cut timber is known as ‘green’ timber)
- The wood is then seasoned (slowly dried to reduce moisture content to prevent warping, splitting, and mould, and to make it easier to paint and glue)
- Wood is stacked with spacers (creating small gaps between them)
- Can be air dried (takes ages) or kiln dried (faster – with controlled temperature and humidity)

- Once dry, wood can be put through a thicknesser which planes the outside smooth (or it can be left rough-sawn)
- Can be joined and machined in many ways

Common Timber Stock Forms

- Boards / planks (rectangular cross sections in a range of common sizes, i.e. 100x50mm; various lengths)
- Dowelling (cylindrical rods)
- Moulding (decorative pieces for running along skirting boards and along furniture edges etc; range of profiles/shapes)
- Posts (square, round, half or quarter circle cross sections)
- Beams (larger, thick structural pieces used for supporting a roof etc
- Wider slabs can also be cut (maximum width of tree trunk)
Properties of natural timber
- Snaps easily along grain lines, but is strong in other direction
- Can have irregular strength, due to knots and grain
- Generally has good tensile strength and compressive strength
- Size and cross-sectional shape impacts strength
- Different tree species have wood with different properties and are suitable for different purposes
- Comes in two types: softwood and hardwood
Softwoods
- Come from conifers (have seeds in pinecones not a fruit or nut)
- Usually evergreen
- Typically grow faster (rings/grain lines are further apart) – hence cheaper
- Not necessarily softer (although most are)
- Commonly used in construction, paper production and general purpose repairs
SOFTWOODS
Pine
Properties
Uses
Douglas Fir
Properties
Uses
Western Red Cedar
Properties
Uses
Macrocarpa
Properties
Uses
Other softwoods include Spruce (common in the UK and Scotland – lightweight and strong, but harder than Pine).
Hardwoods
- Come from angiosperm trees (flowering)
- Lose their leaves in winter
- Grow slower and typically have prettier grain
- Often preferred for fine furniture, flooring, and decorative items
- Many are indeed hard and dense, but not always (for example, balsa wood is a hardwood, yet is one of the softest and lightest woods available)
HARDWOODS
Oak
Properties
Uses
Walnut
Properties
Uses
Beech
Properties
Uses
Saligna
Properties
Uses
Teak
Properties
Uses
Ash
Properties
Uses
Balsa Wood
Properties
Uses
Other hardwoods include Mahogany (durable, rare, and expensive – used for good quality furniture and jewellery boxes).
Manufactured boards
- Composite materials
- Stock forms: typically come in wide flat sheets at standard sizes (i.e. 1200 x 1800mm)
- Less environmentally friendly to dispose of, as can involve the addition of glues/binders containing toxic chemicals (but often use up scraps / offcuts, so can be less wasteful)
- Relatively cheap
- Readily available
- More uniform in strength, because don’t have grain running through them in one direction or knots to provide weak points
MANUFACTURED BOARDS
Veneer
Properties
Uses
MDF
Properties
Uses
Chipboard
Properties
Uses
Hardboard
Properties
Uses
Plywood
Properties
Uses
Blockwood
Properties
Uses
Engineered wood
Properties
Uses
Laminated veneer lumber
Properties
Uses

Environmental factors
- Timber is a renewable resource – trees can be replanted
- Timber is biodegradable (rots away easily)
- Some manufactured boards and tanalised/treated timber have toxic chemicals
- Plantations should be managed responsibly to avoid deforestation, i.e. replanting more trees after they are cut down
- New Zealand has issues with the offcuts, branches, and other debris (known as ‘slash’) clogging up streams, rivers, and beaches. This can harm marine life, damage riverbeds and bridges, and contribute to erosion. Logging operations need to be managed responsibly
- Manufactured boards can use recycled timbers or use up offcuts that would not otherwise be used, minimising waste
- Some products are created using recycled timber – provides a marketing opportunity
- In general, timber is far more environmentally friendly than other materials

Sample examination questions (AS Design & Technology)
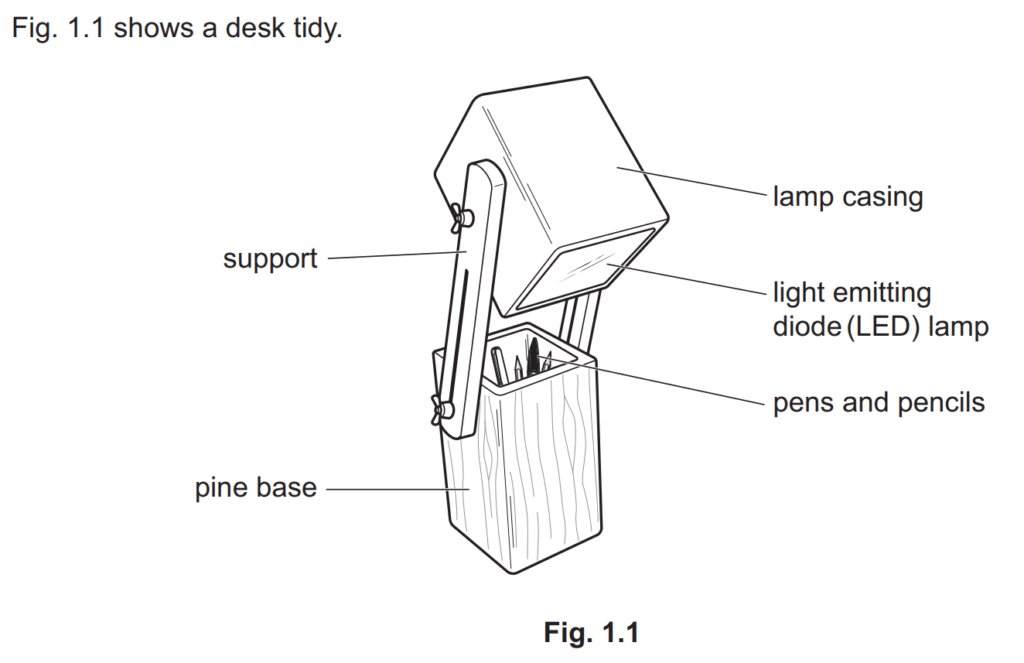

Examiner comment: Most candidates were able to describe a property of pine that made it suitable for the base of the lamp. Many candidates correctly referred to how easy it would be to cut, shape or join the material, the aesthetic qualities of the material, its sustainability or that it is relatively inexpensive to purchase compared to a hardwood. For the award of both marks, a clear description of the property was required, for example that pine can be given a coat of clear varnish that will enhance the appearance of the grain and provide an attractive finish.
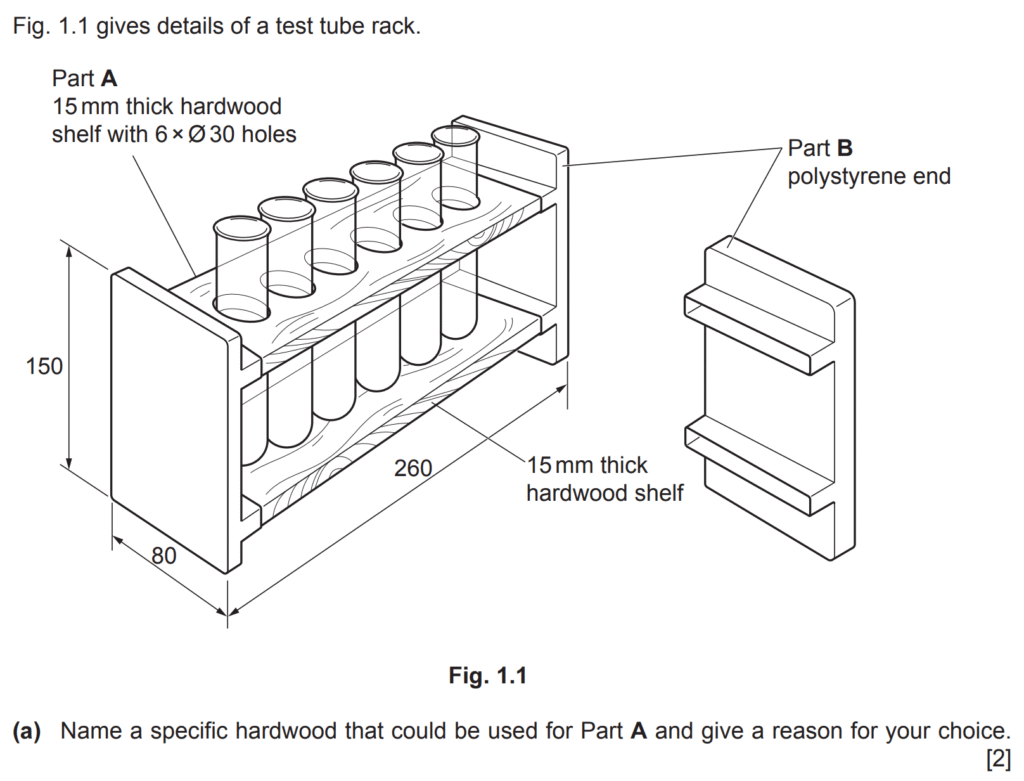

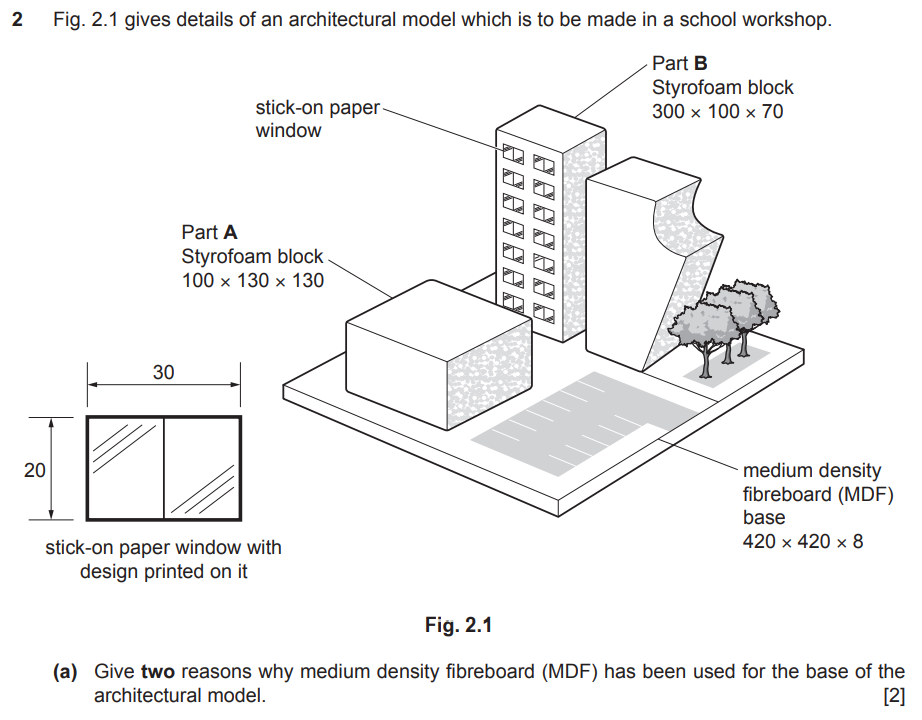
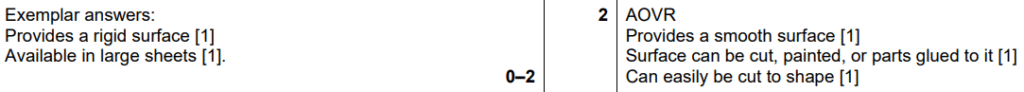
Examiner comment: Most candidates were able to correctly explain at least one reason why MDF had been used for the base of the architectural model, with providing a smooth, rigid surface and being easily cut as popular answers.
