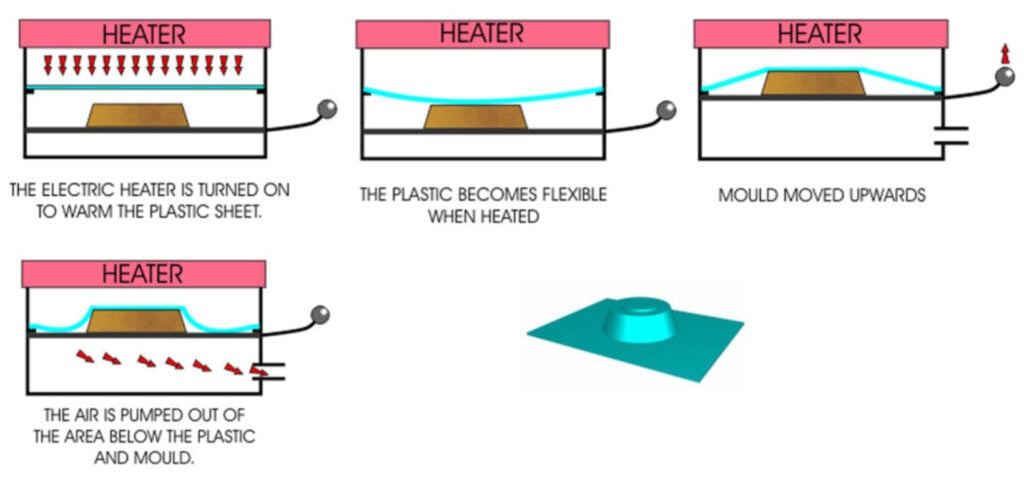
Vacuum forming process
- The former is placed on the bed of the vacuum former (avoid placing former directly on top of air holes)
- A thin sheet of thermoplastic is clamped into position above the mould (i.e. PVC)
- The heater is turned on
- The plastic becomes soft and flexible, the heater is turned off and the mould moved upwards by a lever
- The mould is moved upwards and the vacuum turned on (or the handle pumped) to suck out the air beneath the plastic sheet, drawing it tight down around the mould (former)
- The vacuum former is turned off
- When the plastic has cooled, the item is removed from the machine and the former extracted
- Excess plastic can be trimmed with scissors or a scroll saw, and rough edges smoothed with sandpaper or a file
Guidelines for the former (mould)
- Use draft angles (slightly angled sides of at least 3 degrees) to make removal of mould easy
- Have rounded corners to aid removal of mould
- Can have air holes in complex moulds to help plastic get sucked down into complex shapes
- Can use a release agent
- Must be relatively simple
- Former can be made from a heat-resistant, non-meltable, easily shapeable material such as MDF or pine
Why is vacuum forming useful in packaging products?
- Offers product protection: Vacuum forming allows for the creation of custom-fitted packaging that precisely matches the contours of a product. For instance, a set of art supplies might be packaged in a vacuum-formed tray that holds each item securely in place, preventing damage during shipping and handling. This is particularly important for delicate items like paintbrushes or fragile drawing tools.
- Cost-effectiveness: For medium to large production runs, vacuum forming can be a cost-effective packaging solution. Once the initial mould is created, it can be used to produce large quantities of identical packaging quickly and efficiently.
- Durability: Vacuum-formed packaging is often more durable than traditional cardboard options. For products that may be stored for extended periods or subjected to rough handling, such as craft kits or model-making supplies, a PVC vacuum-formed packaging can provide better long-term protection and maintain its shape and appearance over time.
- Transparency / visibility of product: Vacuum forming allows for the use of clear materials, enabling customers to see the product without opening the packaging. This is particularly useful for items where visual confirmation of the contents is a key factor in the purchasing decision. For example, transparent blister packaging is a very common and effective packaging strategy that allows clear visibility of the product.
- Hygienic properties: Vacuum-formed packaging, especially when using appropriate thermoplastics that provide a hygienic, waterproof surface such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offers excellent protection against bacteria and contaminants. These materials are particularly suitable for packaging items that require a clean, easily sanitised environment, like medical supplies, food products, or children’s toys.
- Lightweight: Vacuum-formed packaging can be lighter than alternative packaging methods. This can reduce shipping costs and make the products more convenient for consumers to carry and transport.
- Moisture resistance: Vacuum-formed plastic packaging offers good moisture resistance, which is crucial for protecting items like paper products, water-soluble art supplies, or items that could be damaged by humidity. This feature ensures that products remain in good condition during storage and transport. Repeatability of the same shape for batch or mass production allows a quick, easy, and cost-effective package to made.
Why PVC and acrylic have good properties for vacuum forming.
- Meltable / thermoplastic: The fundamental property that makes PVC and acrylic suitable for vacuum forming is their thermoplastic nature – they soften when heated and harden when cooled. This characteristic is essential because it allows the material to be shaped without changing its chemical composition. For example, in the production of blister packaging for consumer goods, PVC can be repeatedly heated and shaped while maintaining its original properties.Both materials have specific temperature ranges at which they become pliable enough for forming but don’t degrade. This property is crucial because precise temperature control determines the success of the forming process.
- Thickness uniformity: Both materials can maintain relatively uniform thickness when stretched during the vacuum forming process. This property is vital because it ensures structural integrity in the finished product. When forming PVC sheets for packaging trays, the material stretches predictably, maintaining sufficient thickness even in deeply drawn areas.
- Glossy, shiny appearance: PVC and acrylic both have excellent surface finish properties that are maintained after forming. This characteristic is important for aesthetic and functional reasons. Vacuum formed acrylic display units, for example, retain their glossy appearance and smooth surface even after the forming process.
- Durability: Both materials exhibit good durability and resistance to everyday wear and tear after forming. This property is essential for creating products that maintain their shape and function over time. Vacuum formed PVC signage, for instance, can withstand various weather conditions while maintaining its formed shape.
- Range of colours and transparency: Both materials can be manufactured in various colours and transparency levels that remain stable through the forming process. This versatility is important for aesthetic and functional requirements. Clear acrylic remains transparent after vacuum forming, making it perfect for display cases or protective covers.
- Impact resistance: These materials maintain good impact resistance after forming, though acrylic is generally more brittle than PVC. This property is important for durability in end-use applications. PVC’s better impact resistance makes it suitable for protective packaging and durable consumer goods.
- Waterproof: Both PVC and acrylic are naturally waterproof and maintain this property after vacuum forming. This allows the materials to be used in applications where water resistance is essential. For example, vacuum formed shower trays, bathroom fittings, and outdoor signage made from these materials can withstand constant exposure to water without degrading or losing their shape. PVC is particularly valued in food packaging applications where moisture barriers are needed to protect contents.
- Recyclability: Both materials can be recycled, although their thermoplastic nature means they may degrade slightly with each reprocessing cycle. This characteristic is increasingly important due to environmental considerations. Vacuum formed PVC packaging can be recycled, though the quality of the material may decrease with repeated processing.
