Understanding the properties of materials is fundamental for Design & Technology students as it helps you to select which materials are appropriate for which task. This article provides a list of properties and definitions, with examples to help students become familiar with these terms.
Material properties
Rigidity / Stiffness
- Resistance to deformation under an applied force
- Describes how much a material deflects or bends when subjected to a load
- Examples: steel beams, hardwood, thick glass, foamboard
Hardness
- Resistance to surface pressure (denting, scratching)
- Firm, solid and compact
- Not easily cut
- Examples: hardened steel, granite, saligna (wood from a type of gum tree)
Toughness
- Strength, durability, resilience
- Ability to withstand great strain without tearing or breaking
- Examples: high-impact polystyrene, leather
Brittleness
- Resistance to impact
- Tendency to snap / shatter
- Examples: glass, ceramic, cast iron
Elasticity / Flexibility
- Ability to bend or stretch and return to original shape
- Examples: rubber bands, springs, elastic fabrics
Ductility
- Ability to be pliable and flexible
- Can be deformed under tensile stress (stretching or pulling)
- Examples: copper, silver, gold, aluminium which can be made into thin wire
Malleability
- Ability to be hammered or pressed into shape without breaking
- Can be deformed under compressive stress
- Examples: gold, copper, lead, aluminium foil
Dimensional Stability
- Ability to retain its shape / existing dimensions when subjected to various stresses
- Examples: engineered wood, stainless steel
Corrosion Resistance
- Resistance to oxidation / degradation (rust / decay)
- Examples: stainless steel, aluminium, PVC
Electrical Conductivity
- Ability to conduct electrical current
- The opposite of insulating materials which resist electrical flow (rubber and plastic are good insulators)
- Examples: copper, aluminium, silver, gold
Thermal Conductivity
- Ability to conduct (transmit) heat
- Examples: copper, steel, aluminium
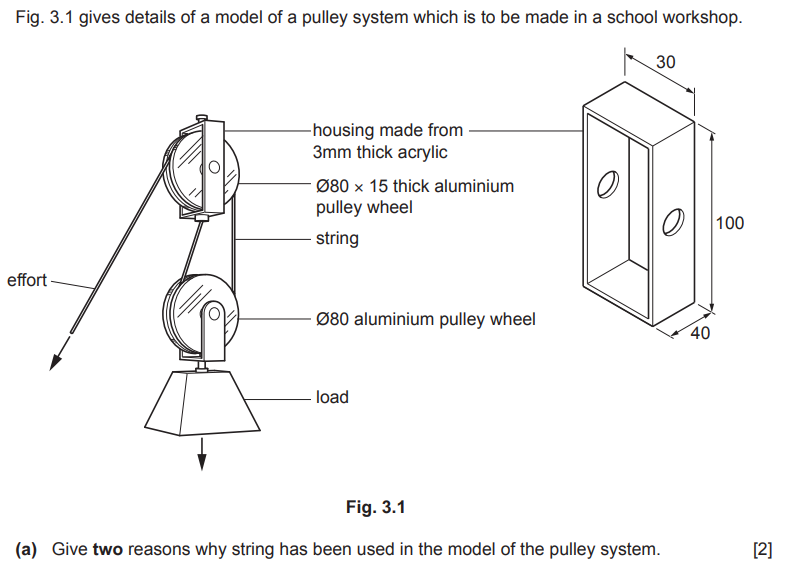

Examiner comment: Most candidates could give at least one reason for using string in the model of the pulley system.
