High school Design & Technology students are often required to be familiar with the how computer aided design (CAD) is used in industry to generate 2D and 3D images, as well as digital simulations. Students should also be familiar with how other digital technologies, such as video conferencing software, can help aid the design process. This article outlines the advantages and disadvantages of CAD for designers, and introduces students to common software programmes. It concludes with sample examination questions, helping students to revise this material.
The advantages of CAD over manual drawing for a designer or design firm
- Increased efficiency and speed
- Easy to make modifications (can crop, edit, or enhance, without needing to redraw)
- Easier to organise and find work when stored on a computer – images and data can be sorted into folders and named – files can be easily searched for by name, date or other identification tags.
- Can use a digital library of common parts (don’t need to draw each item from scratch) or import backgrounds, working faster
- Can easily copy and paste repeated elements, saving time
- Enhanced accuracy and precision
- Can work to the precise pixel – perfect accuracy
- Can repeat identical aspects exactly, by copying and pasting
- Can undo errors instantly
- Better design visualisation
- Product can be rotated and viewed in 3D and from different angles (virtual reality)
- Can zoom in and out to see more detail
- Can turn off / on layers to show / hide different parts of the drawing as required
- Improved collaboration
- Easy to email and share designs and feedback (can also share design proposals with wider public via social media)
- Team members and clients in different locations can collaborate and work on the same project at once
- Cost savings
- Can simulate real-world product testing without the cost or danger of real-world tests (i.e. performance in an earthquake)
- Less office space needed for storage than when using hardcopy drawings / models – computer can store thousands of images without running out of space
- Staff can work remotely, requiring less office space
- Allows computer aided manufacture (CAM) helping with creating multiple identical items increasing quality and efficiency of small batch and mass production
The disadvantages of CAD drawings for designers
- Expensive hardware and software required – large investment required
- Specialised expertise is needed – can have a big learning curve
- Software may become obsolete – requiring investment in new software, or file types that are no longer compatible
- Technical vulnerabilities – files may become corrupted, computers may crash, power outages may result in lost work (need regular backups)
- Ideas can be more easily stolen by others when shared online
Ways images, fonts, or other graphics can be captured and stored on a computer
- Upload from a digital camera or mobile phone (input device) and then saved to a folder
- Hand drawn, then scanned, sent to a device, and saved to a folder
- Keyboard shortcuts or tools (like Snipping Tool) can screenshot an image of the screen and save it
- Downloaded from the internet – searching for freely available images/fonts/textures (or paying for licensing) and these saving these from websites to a folder
- Imported from removable media such as transfer images from USB drives or external hard drives to the computer
- Images can be backed up – copied to cloud storage or external drives for safety.
Ways image manipulation software (such as Adobe Photoshop) can be used by designers:
- Crop and scale imagery
- Modify and enhance existing imagery (adjusting contrast, colour hue and saturation etc)
- Resize the file, ensuring a suitable resolution / number of pixels for printing, such as 300dpi (dots per inch), or 72dpi for sharing online
- Apply lettering and other graphic design elements
- Create new imagery
- Prepare files for sending to clients
- Prepare files for output devices such as various digital printers or CAM tools
Note: AI integration is also advancing at a rapid rate, now allowing designers to generate imagery from text alone.
Digital designs can be:
- 2D – such as orthographic working drawings created using technical drawing software such as AutoCAD, or graphic design spreads / book layouts created using desktop publishing software such as Adobe InDesign
- 3D – such as a 3D representation using Sketchup, or realistic rendered pictorial imagery created using 3D modelling software such as Blender
- 4D – animations or simulations / virtual reality experiences created using software such as Unreal Engine (time is considered the 4th dimension – the integration of movement) and are discussed in more detail in the article about emerging technologies
Common Software used by Designers
In addition to using digital design software, designers often use a wide range of software to communicate with clients, staff members and other stakeholders:
- Writing tools – such as Microsoft Word
- Data analysis tools – such as Microsoft Excel
- Presentation tools – such as Microsoft PowerPoint (for making slideshows) and Adobe Acrobat Pro (for editing and publishing PDFS)
- Email, messaging, and collaboration tools – such as Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Teams, Miro and Skype for video conferencing

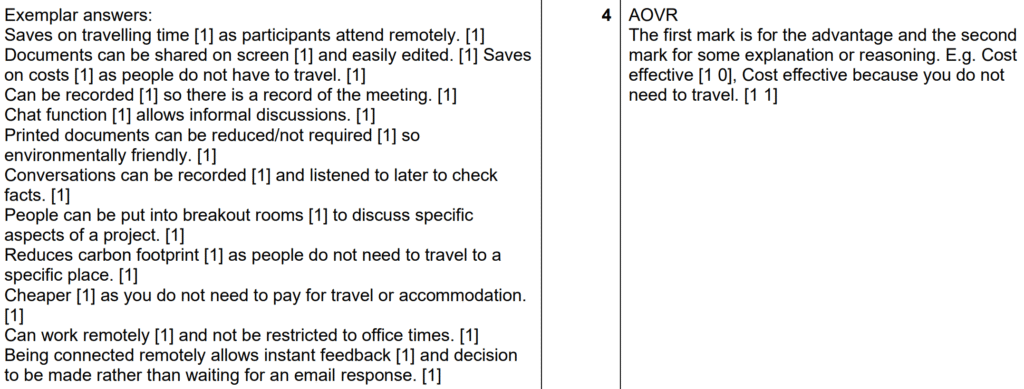
Examiner comment: Many excellent responses were seen to this question. Common advantages for designers using video conferencing to discuss a design proposal included that travelling time and costs are reduced as participants can join remotely from anywhere in the world, that documents can be shared on screen and collectively edited, that discussions can be recorded so that they can be referred to at a later date, that the chat function allows informal discussions and instant feedback and that it is more environmentally friendly as printed documents are not required. Only a very small number of candidates appeared to have little understanding, or experience of using, video conferencing.
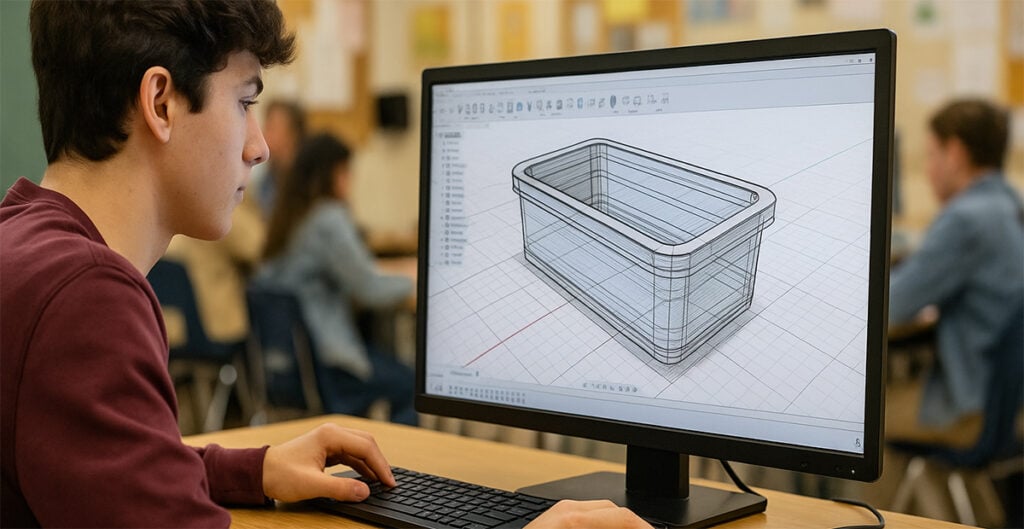
Discuss why designers of packaging use CAD (computer aided design) to develop and communicate design proposals.


Examiner comment: Most candidates were able to explain why designers use CAD to develop and communicate ideas. Candidates who discussed issues such as how easy it is to share CAD design proposals with customers, the speed of construction on CAD as well as the ease of deleting mistakes or indeed editing a design answered well. Examples were not always given.
