Planning drawings help designers and manufacturers organise and manage projects from initial concept through to final production. They provide visual methods for planning timelines, documenting processes, and organising resources. Planning drawings enable designers and manufacturers to coordinate complex projects efficiently, anticipate problems, and communicate plans clearly to team members, helping to ensure projects stay on schedule, within budget, and meet quality standards.
Common planning drawings include gantt charts, flow charts, and parts lists with assembly drawings.
Gantt Charts
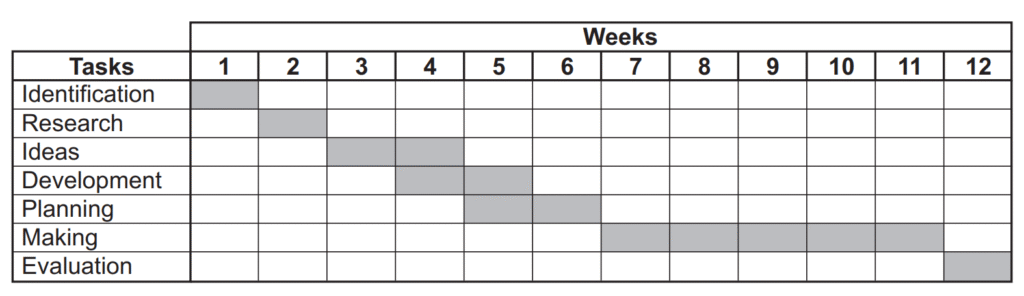
Gantt charts are useful in design & technology for:
- Visualizing project timelines – showing when different stages of production will occur (and helping organise these, identifying which tasks must be completed before others can start)
- Tracking progress – monitoring whether the project is on schedule and helping to meet deadlines
- Coordinating teams – ensuring all the different team members (designers, engineers, and manufacturers) work in sync and understand what is expected
Learn more about Gantt charts here
Flow charts
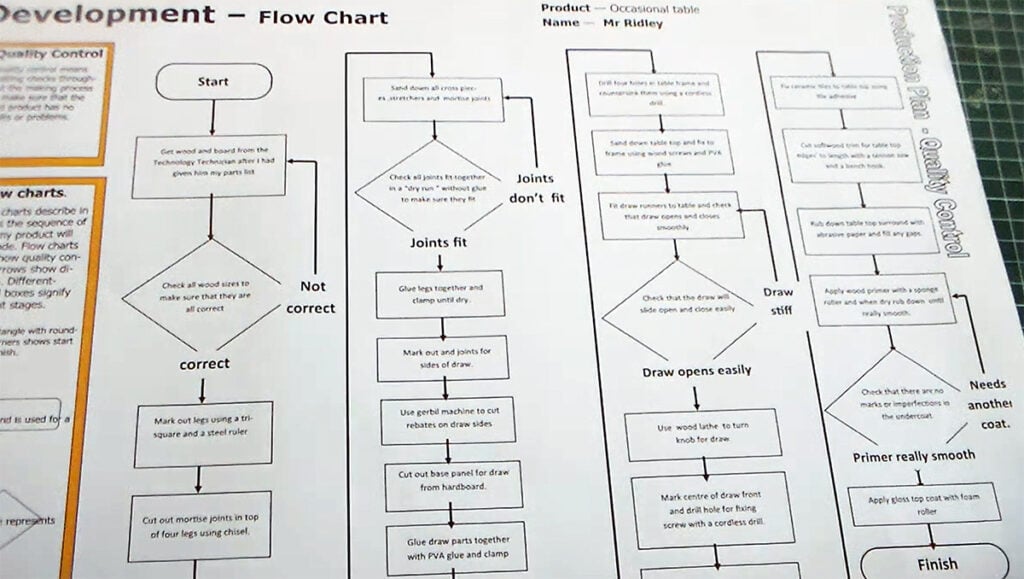
Flow charts are useful in design & technology for:
- Planning the construction process – used by a designer to clearly show the stages in the manufacturing process, ensuring all stages of manufacture are thought through and in the correct order
- Mapping user flows – showing how users navigate through an app or website, or use a product
- Identifying problems – revealing bottlenecks, problems, or confusing aspects of a design process or construction sequence
- Team alignment – ensuring everyone understands the expected process
Learn more about flow charts here.
Parts lists and Assembly drawings
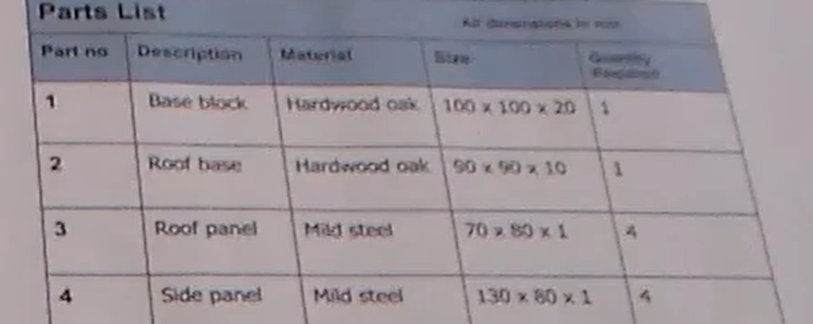
Benefits of parts lists:
- Resource planning – shows the material, size and number of parts required to make a product, helping you identify all components and fixings needed before manufacturing begins, preventing delays caused by missing parts, and avoiding ordering of too many parts (minimising waste)
- Cost control – enable accurate budgeting and help keep projects within budget
- Quality assurance – specifying exact materials and standards required helps maintain consistency and quality
- Assembly guidance – ensure assembly process is understood and no components are overlooked or missed during construction
Learn more about parts and assembly drawings here.
Note: According to the Cambridge syllabus, an orthographic drawing is not a planning drawing.
Sample examination questions (AS Design & Technology)
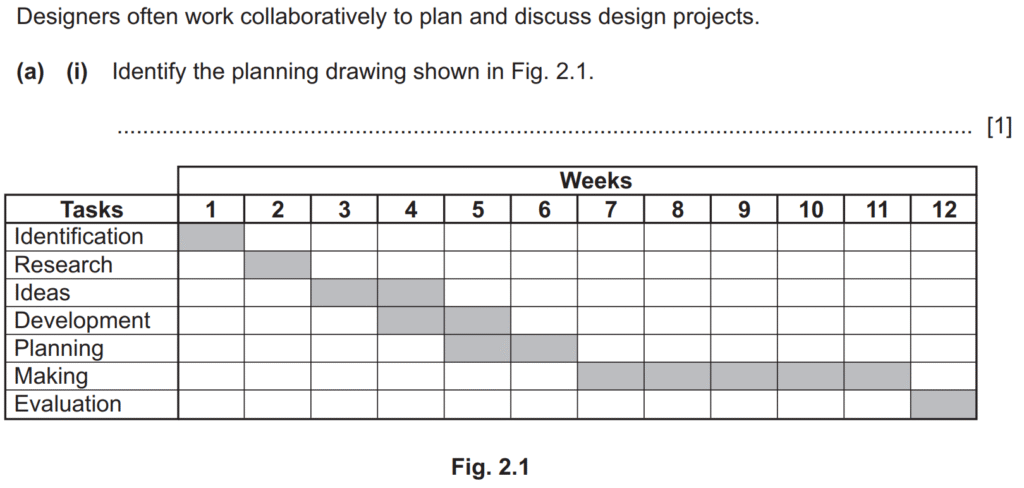

Examiner comment: Most candidates were able identify the given planning drawing as a Gantt chart. Some candidates incorrectly stated that it was a chart or a design process chart.


Examiner comment: Common correct answers were a flowchart, cutting list or materials list. The explanation of why a flowchart would be used by a designer often referred to it clearly showing the stages in the manufacture of a product in the correct order. The explanation of why a materials list or cutting list would be used by a designer often referred to these clearly showing the material, size and number of parts required to make a product. Common incorrect answers were often based upon naming and then explaining a type of drawing that was not a planning drawing, for example an orthographic
drawing or an exploded drawing.
